Do you know? Diversification of assets is the most important thing in investments. Moreover, diversification includes various types of asset classes. Of all the asset classes, a Bond is one of the important assets to have in a portfolio. This can give better returns than FD. let’s discuss how to invest in bonds in detail.
Dear Reader, Welcome to SimplyRead! Yes, here things are So Simple!
WHAT IS BOND?
Generally, a Bond is a contract made between the buyer and seller based on certain conditions. Simply put, a Bond is an agreement. Likewise, Companies that intend to generate revenue can make a contract with the investor based on a fixed interest rate. Moreover, these bonds can be viewed as a loan the company is taking with the help of investors.
WHY INVEST IN BONDS?
Firstly, for expanding the company, the company’s management needs capital. Secondly, these funds or capital can be raised through loans from banks, listed companies in the share market, etc. However, the bank loan will impose a high-interest rate on the borrower. Also, some companies wish to have all the stakes within the company and don’t list the company in the market. To handle this differently, companies can get loans from investors at a cheaper interest rate compared to bank loans. Finally, the strategy of getting a loan from investors is called a bond.

Since both the company or issuer and the investor get good interest rates, bonds can be considered a Win-Win.
TERMINOLOGIES
Let us cover the various terminologies involved in bonds as follows.
->ISSUE SIZE
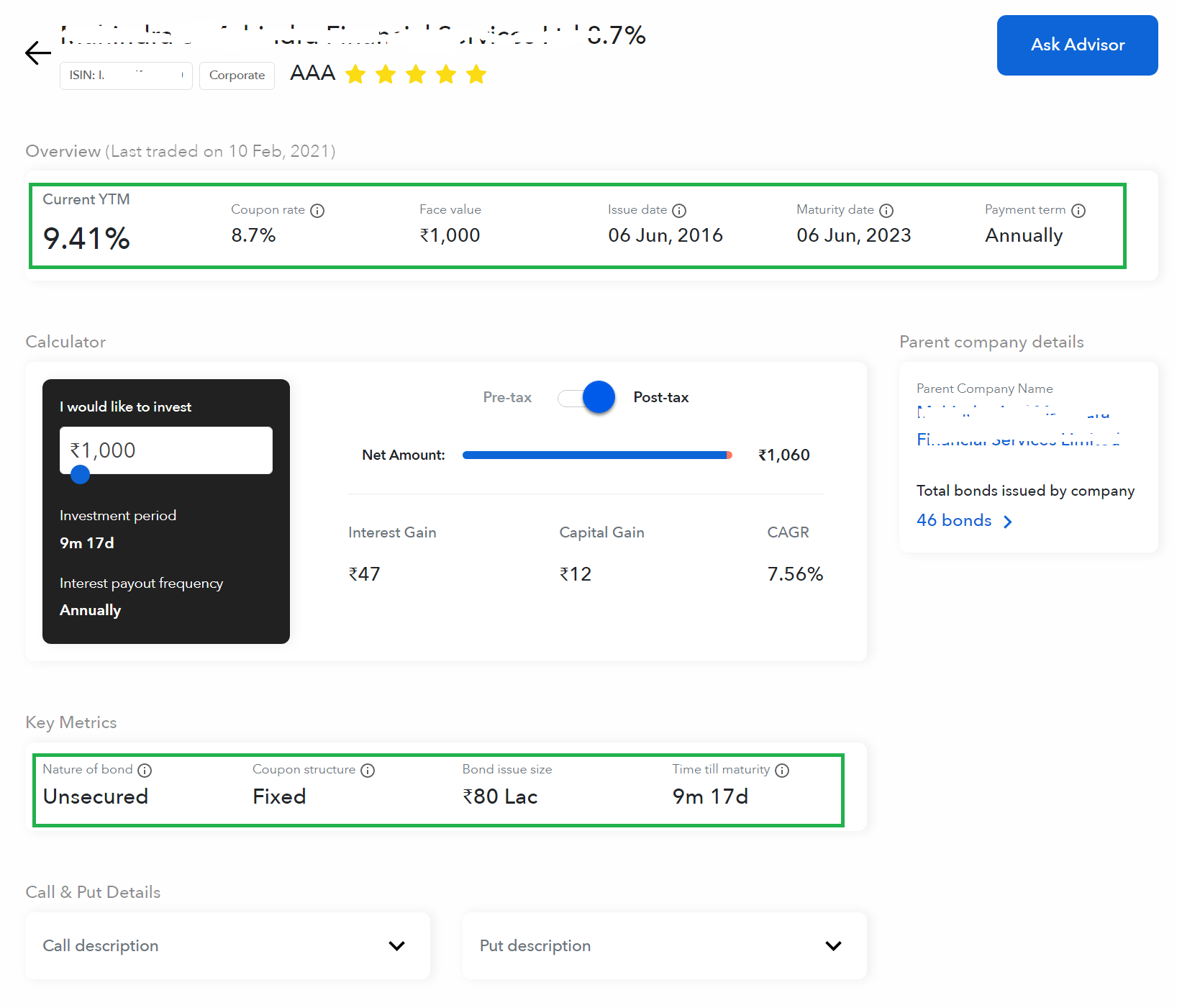
Issue size can be derived by multiplying the number of bonds issued with the face value. Moreover, Issue size determines the amount needed for the company from the investor. Simply put, the total value needs for the company from investors.
->ISSUE DATE
The issue date is the date at which the bond is issued to the investors. In other words, it is the date at which the bond starts to yield interest to the investors.
->FACE VALUE
The face value of the bond is the price paid by the bond issuing company at the time of maturity. Simply put, it is the promised sum to be paid to the investor at maturity. It is also called a Par value.
->COUPON RATE
The coupon rate is nothing but the interest rate provided for the bond. Moreover, the interest rate is fixed but varies from one bond to another. Also, the interest payout can usually be made twice a year. However, Interest payout frequency depends on the issuer’s commitment to the investor.
For example, consider I am investing ₹10000 in a Bond and its coupon rate is 5%. Therefore, I would be getting ₹500 as interest payout.
->MATURITY DATE
Like Fixed Deposits, Bonds have a maturity date at which the bond matures. Additionally, the principal will be paid to the investor at the time of maturity. Simply put, the investor gets all his/her money invested at the time of maturity.
Note: The maturity date may vary when the bond is purchased after the issue date from the open market.
->CREDIT RISK/RATING
Credit Risk/Rating represents the worthiness of the Bond. Additionally, it is the rating given by the financial rating agency considering the strength and weakness of the issuer. In India, there are credit agencies available such as CRISIL, SMREA, ICRA, CARE, etc. The good the rating the bond is safest or less risky.
For example, CRISIL gives the credit rating as AA+, AAA, AA-, etc. which defines the review or potential of the bond.
->COLLATERAL TYPE
Collateral type is the type of collateral that backs the Bond value. Moreover, this collateral can be utilized whenever the company fails to pay interest to the investors. For example, consider an instrument manufacturing company issues a bond. Additionally, this company plans to keep collateral as an instrument’s rental income. If the company fails to pay interest or maturity value to the investors, it can utilize this rental income.
It is always advisable to select bonds that have collateral defined.
TYPES OF BONDS
Bond types depend on the type of the bond issuer. Some of the bond types are as follows.
->CORPORATE BONDS
Corporate bonds are bonds issued by a corporate company. Instead of getting loans from bank corporates uses bonds to raise fund.
->GOVERNMENT BONDS
Government bonds are the bonds issued by the state or central government. Since this is backed by the government, security is high. Therefore, You’re in safer hands. Further, these are named as G-Sec bonds.
->CONVERTIBLE BONDS
Convertible bonds are hybrid bonds that offer the investor interest on bonds and exposure to equity. However, it cannot have both at the same time. Further, depending on the situation the bonds can be converted. Also, convertible bonds can be further classified into many types such as vanilla, reversible, mandatory convertible bonds, etc.
For example, if the share market surges the investor can withdraw the funds before maturity. On the contrary, if the share market falls drastically, the investor can wait for the bond maturity. Accordingly, the bond can be converted.
->FRSB/RBI BOND
FRSB 2020 or Floating Rate Savings Bond is issued by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in which the interest rate fluctuates with the economic rate. Moreover, this bond offers an interest payout for half a year. Also, there is another savings RBI bond which offers a fixed interest of 8% and was incorporated in 2003.
Note: RBI Bonds apply only to Indian citizens.
FRSB2020 Link: https://www.rbi.org.in/Scripts/NotificationUser.aspx?Id=11923&Mode=0
RBI Savings Bond Link: https://rbi.org.in/Scripts/BS_ViewSavingBonds.aspx?Id=1116#:~:text=Maturity%20and%20rate%20of%20interest,1601%2F%2D.
->ZERO COUPON
Zero coupon bonds provide zero interest payout. However, the bonds provide interest at the time of maturity.
->INFLATION-LINKED
As the name says, Inflation-linked bonds are associated with the inflation rate of the country. Moreover, here both the interest and principal fluctuate according to the inflation rate. It can be bought directly from the government. Ultimately, the purpose of this bond is to beat the inflation rate of the country.
->SOVEREIGN GOLD BONDS
Sovereign Gold Bonds are issued by the government of India which invests in gold. Click here to read more about investing in Gold.
HOW TO INVEST?
Investing in bonds can be made either through the primary or secondary market.
->PRIMARY MARKET
The primary market is the place where the bonds are issued for the first time by the issuer. Moreover, the buyer can directly buy the bonds from the issuer. Simply put, it is similar to IPO in the stock market. Click here to read more about the basics of the stock market.
For example, corporate bonds and government bonds can be bought directly from the issuer.
->SECONDARY MARKET
The secondary market is the place where the bonds can be traded publicly. Moreover, the bonds can be bought and sold from the people using the Demat account. Simply put, bonds can be traded like stocks. These bonds can be bought and sold through a broker, Bank account, Demat account, etc. Also, some brokers such as WintWealth, Indmoney specifically deal only with bonds. Click here to read more about Demat account. Also, there are mutual funds which invests in bonds.
For example, Government securities are represented as G-SEC and T-bills in the Demat account. Also, there are mutual funds that invest in different types of bonds.
TO WRAP THINGS UP!
Investment in bonds is essential for investors who wish to diversify their portfolio. It is advised that 50% of the total investment should go to bonds. As a result, the investor can protect his/her portfolio from disasters.
Choosing the type of bond depends on personal wishes. What type of bond you are going to invest in?
Thanks for reading. So Simple!