What comes to your mind when you hear the word Mutual Fund? For me, the sentence read in 3x speed. Mutual funds are subject to market risk, read the documents carefully before investing. If your mind thinks about multiplying money, then you are at the right place. Let’s discuss about the Mutual Funds in detail.
Dear reader, Welcome to SimplyRead. Yes, here things are so simple!
FACT: A Demat Account is not mandatory for investing in Mutual Fund.
Click here to learn about Demat account.
WHAT IS A MUTUAL FUND?
A mutual fund refers to collecting money from a pool of investors and investing them in the securities such as Stocks, Bonds, Commodities, etc. Additionally, there will be a fund manager who manages the invested fund effectively.

To understand this simple, let’s take an example of a travel agency. The travel agency takes care of all the needs for travel, stay, sight-seeing, food, etc. However, why can’t people plan themselves? Because, for a trip to an unknown foreign country, People might not have proper knowledge of these things. Therefore, they need the help of an agency. Likewise, people who don’t know about Investing instruments like stocks, bonds, etc. can lend the money to Mutual funds. As a result, the fund manager will take care of the invested funds similar to the travel agency.
Now, this agency has to charge some fee for their service right? Absolutely, yes. The investor needs to pay the service charge for Mutual funds as well. Because Nothing is free in this world! These charges may include Entry load, Exit load, Total expense Ratio (TER), etc. will be discussed below.
TYPES OF MUTUAL FUNDS
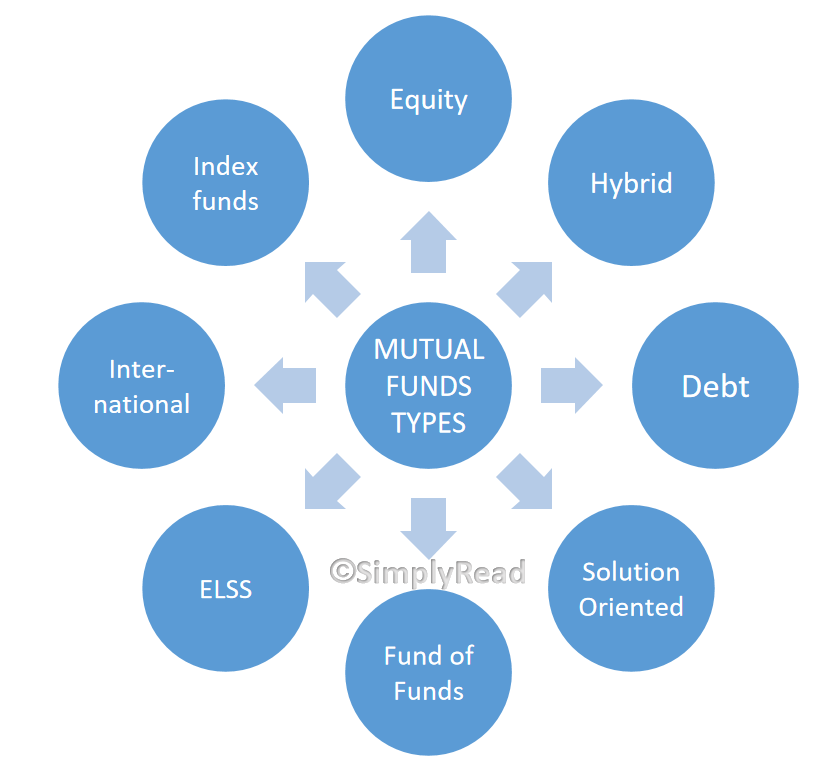
We love varieties in almost everything such as food, apparel, movies, etc. Because variety gives purpose and fun. Likewise, in Mutual Funds, there are a variety of funds that serves their purpose. Let’s make it simple!
- EQUITY: Equity mutual funds are the funds that invest in stocks. This can be further classified as Small Cap, Mid Cap, Large Cap, Flexi-Cap, and others. According to the individual’s risk profile, the investor can choose the funds.
- DEBT: Debt mutual funds invests in Debt bonds such as corporate and government bonds. This can be of various flavors such as Short duration, Ultra Short Duration, Medium Duration, long duration, etc.
- SOLUTION ORIENTED: The name itself says the meaning of providing a solution to the investor. The solution may be a retirement plan, 40’s plan, Wealth creation plan, Child education plan, etc. According to the need, the risk factor will be decided and invested in the long term.
- HYBRID FUNDS: Hybrid generally means a combination of different variants to make a single entity. Moreover, this single entity reflects the characteristics of the mixed variants. Similarly, Hybrid funds combine equity, Debt, and other asset classes depending on the scheme proposed.
- FUND OF FUNDS: This differs slightly from the hybrid fund. Hybrid funds invest in different asset classes whereas fund of funds invests in different mutual funds. Sometimes, it is also called a multi-manager fund.
- INDEX FUNDS: Index funds invest directly in the indices of the stock market. Thus, the price of the Index funds varies directly with the indices of the market. Click here to read briefly on indices.
- TAX SAVING OR ELSS FUNDS: Equity Linked Savings Scheme (ELSS) is a type of mutual fund which allows saving tax under section 80c. These funds are linked to equity in large proportion and other securities in smaller proportion. Also, many funds give the option to choose the allocation percentage in equity and other securities.
- INTERNATIONAL FUNDS: Mutual funds give you exposure to investing in foreign markets as well. This is nothing but international mutual funds.
HOW MFs ARE PRICED?
We know how stocks are priced based on demand and supply. Click here to read the basics of the stock market and know how stocks are priced. But, MF price is calculated based on the Net Asset Value (NAV) determined at the end of the business day. The formula to calculate NAV is as follows,
NAV = (assets – liabilities) / total number of outstanding shares
Assets: The asset is the total market value of MF such as investments, cash, etc. Liabilities: Liabilities are the pending payment/fees from MF to an entity such as banks and other financial providers. Outstanding shares: Total no. of shares held by investors.
THINGS TO CONSIDER WHILE SELECTING MF
Selecting the MF needs to be done with utmost care before investing in MF. Here are some of the criteria to watch before selecting the Mutual Fund.
- AMC: Asset Management Company (AMC) is the firm that invests the pooled funds from the clients in various investment instruments such as equity and other security. Simply put, it is a mutual fund management company. Investors need to select the company having a good performance history and other criteria as follows.
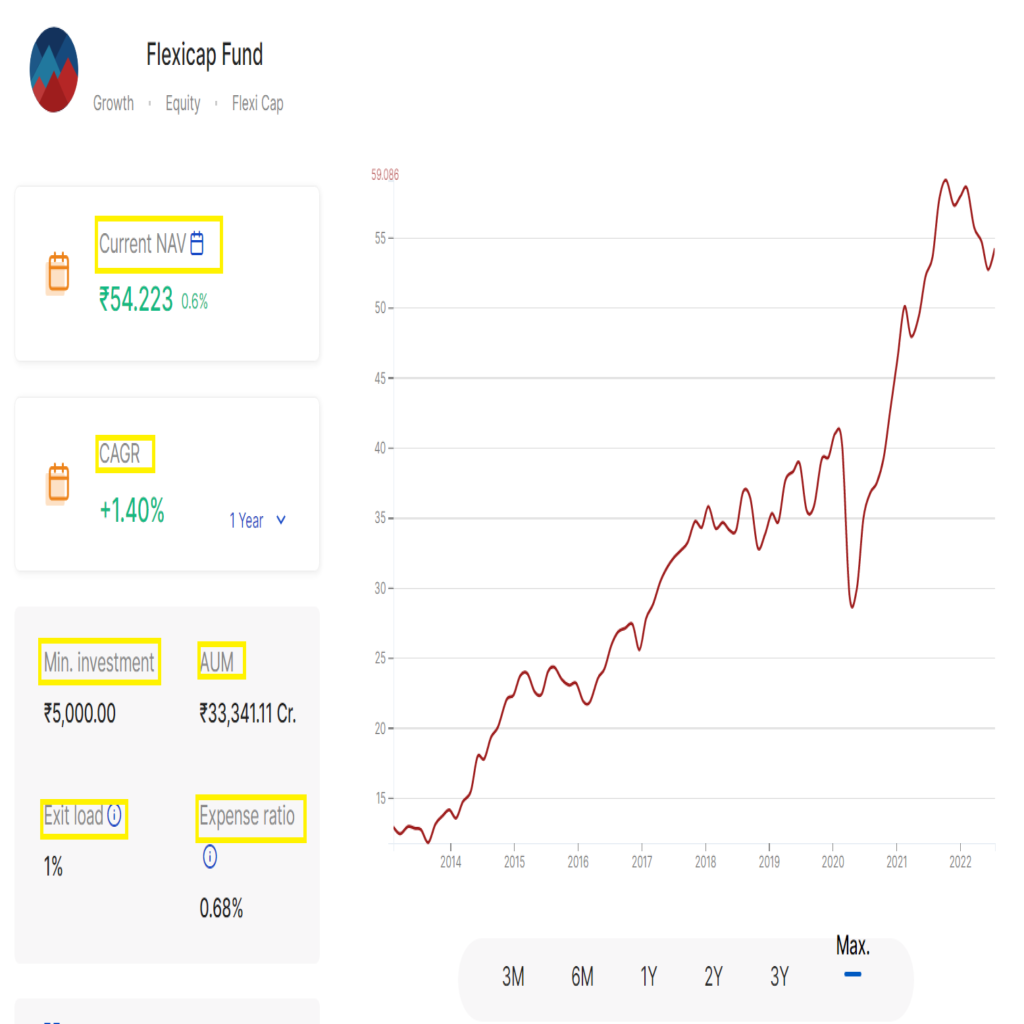
- CAGR: Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) is the annual growth of the investment over a particular period. It is usually represented in percentages and it’s used to track the performance of the mutual fund. A ~15% CAGR over 5 years is considered a good performing mutual fund.
- CATEGORY: Category is nothing but the type of mutual fund discussed above. Choosing the type of mutual fund is an Individual’s choice.
- MIN INVESTMENT AMOUNT: The minimum investment amount for Mutual Fund varies from one fund to another fund. This helps to choose funds based on the individual’s financial status.
- DIVIDEND TYPE: Simply put, Dividends are a company’s profits distributed among the investors/shareholders. MF offers two types namely Growth and Interim Dividend payout. In growth, dividends paid by the company are reinvested in the MF as an investment. On the contrary, the Interim Dividend type pays out dividends to the investor with the frequency as monthly, yearly, quarterly, etc. It’s entirely Investor’s choice.
- TER: Total Expense Ratio (TER) is nothing but the fees paid to the AMC for maintaining the funds invested. This may vary from 0.1% to 3%. Moreover, Choosing a fund having a lower TER is advisable. Because a minimum percentage can give higher returns for a longer period. Click here to read about the power of compounding.
- ENTRY LOAD/EXIT LOAD: Entry load is the fee paid for starting an investment in a mutual fund whereas Exit load is charged while withdrawing money from Mutual Fund. Moreover, Most of the AMCs don’t charge Entry load. On the contrary, Exit load may be charged if withdrawn before a particular period. This period may be 1 year usually and varies between the AMCs/Funds.
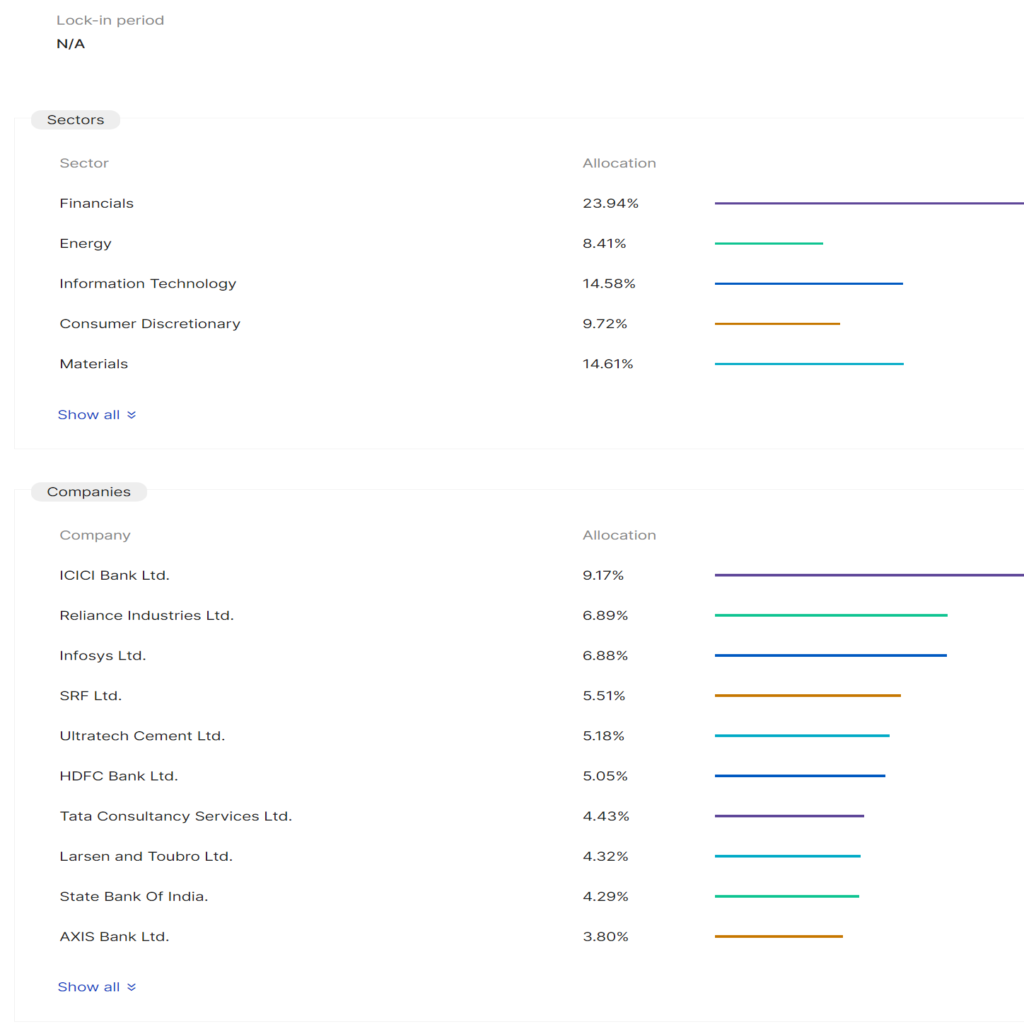
- PORTFOLIO: Watch out for the list of stocks or other securities investment allocation in the portfolio of the Mutual fund.
- AUM: Assets Under Management (AUM) is the total market value of investments managed by the AMC. Mostly, A well-known AMC has a good value of AUM.
MODES OF INVESTMENT
Mutual fund investments can be made through various modes as follows.
- LUMPSUM: Lumpsum is a one-time investment made in Mutual funds and waiting for the investment to grow.
- SIP: Systematic Investment Plan (SIP) is a mode of investment where the investments are made Systematically. Also, SIP can be made daily, weekly, monthly, yearly, etc. of the investor’s choice.
- STP: Systematic Transfer Plan (STP) is a mode of investment where a small proportion of total investment can be transferred to invest in other securities from the same fund house. This is mostly used for transferring low-risk investments to high-risk investments and vice versa.
- SWP: Systematic Withdrawal Plan (SWP) can be explained as withdrawing the invested fund systematically. Simply put, an investor planning for retirement in the 60s can withdraw his/her funds systematically after his retirement like a pension.
- DTP: Dividend Transfer Plan (DTP) allows investors to invest the dividend earned from the investment to different asset classes. For an instance, Dividends paid for debt funds can be utilized for investing in equity funds.


TO WRAP THINGS UP!
I hope We have discussed almost everything about Mutual Funds in this article. What type of fund you’re going to invest in? Do your analysis and proper research while selecting the Mutual Fund.
Use the referral links at the end of the article to open an account for investing in Mutual Funds.
Comment your thoughts/questions in the comment box!
Thanks for visiting SimplyRead– So Simple!
REFERRAL LINKS FOR ACCOUNT OPENING
Click here for referral links.



2 comments